矩形面积并
如图,考虑求图中矩形的面积并
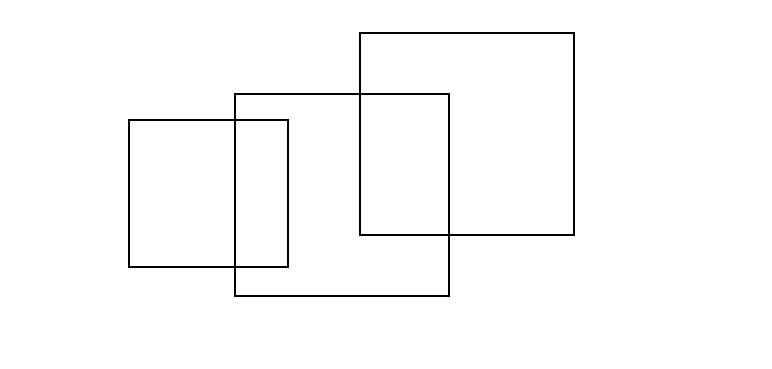
这个问题可以转换成求下图中这些部分的面积
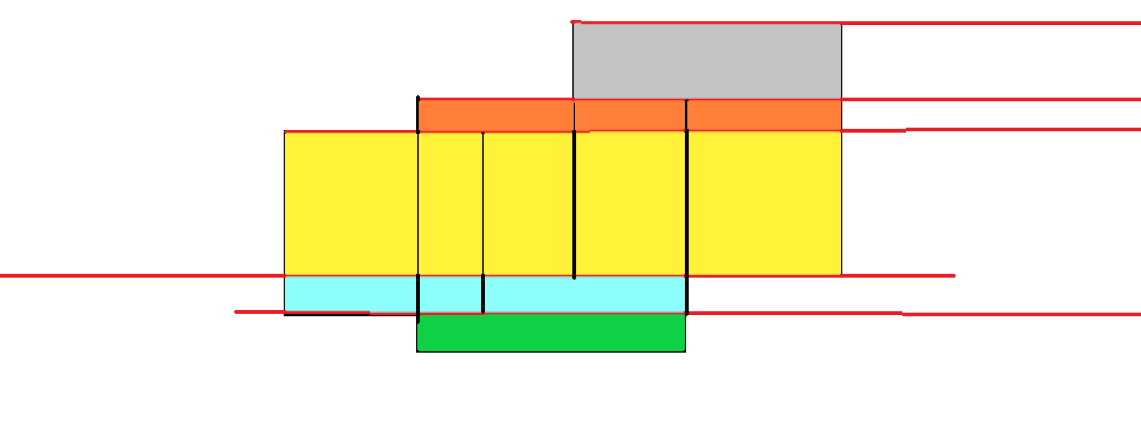
就是从下往上扫一遍,遇到矩形的下边就加入,然后统计当前的线段长度,当然重叠部分的线段只算一次长度,遇到上边就删除,然后每种颜色的矩形面积就是 当前线段长度(将要加入的线段的高度-上一条加入的线段的高度)*
然后这些累加起来就是矩形的面积并
现在的问题就是如何维护当前线段的长度
这里就要用到线段树了
先对矩形的边进行处理,按高度排序,然后下边标记为1,上边标记为-1,然后从下往上扫描
结点信息:
1 | struct node |
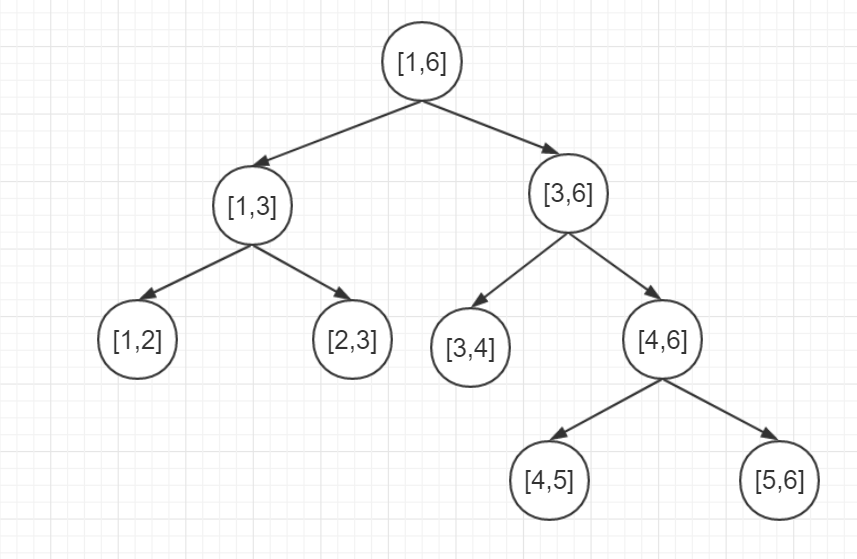
让后当前这个线段树的叶子结点是l+1==r,而不是传统的l==r,因为l==r是一个点这对矩形没有意义
构造线段树
1 | void build (int l, int r, int id) |
这样构造出来的线段树是长这样的
然后是push_up()函数
1 | void push_up(int id) |
有一点很重要,区间是否被完全覆盖是区间自己的事情,即不从子节点更新,也就是说[1,2],[2,3]被覆盖不代表[1,3]被覆盖,但是长度会从子节点更新,所以长度和被完全覆盖是一样的,答案不会错误,换句话说就是结点的s的值不从子节点更新,s的值只会在更新时被自己更新,所以虽然是区间更新,但与传统的区间更新有很大不同,也就不需要lazy tag和push_down
update
1 | void update(int id, int L, int R, int number) |
查询的话,因为只需要知道总的线段的长度,所以只要tree[1].len
例题 HDU-1542
AC代码:这题的坐标有小数,所以需要离散化
1 |
|
重叠矩形的周长
可以和计算面积一样的思路,对于所有的横边扫描一次,周长就是当前的线段长度与上一次的线段长度之差的绝对值
然后对竖着的边也做一次就是周长
例题 poj-1177
1 |
|